The UX design process is a well-orchestrated journey, guiding designers in transforming an initial concept into a functional, user-friendly interface. This carefully structured approach ensures a product aligns with user needs and enhances the overall user experience, making every interaction as intuitive as possible. With its roots firmly planted in understanding and addressing user requirements, the UX design process is divided into critical phases: user research, design, prototyping, user testing, and finally, implementation. This method is inherently iterative, allowing for continuous refinements based on user feedback and emerging insights, ensuring the end product is both effective and engaging.

Navigating through the UX design process demands a keen understanding of several moving parts, including the ever-important stages of developing user personas, wireframing, and the application of tools like UXPin Merge for seamless prototyping. As you delve into the user experience design process, it becomes clear that each step, from initial research to the rollout, is interconnected, with the flexibility to adapt to varying project requirements and goals. By the article’s conclusion, you will have gained a comprehensive overview of how to effectively move from concept to rollout, ensuring your project is well-aligned with both user expectations and business objectives, in the realm of user experience design.
I will provide you with a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to building your next website with excellent user experience.
Table of Contents
Understanding User Needs and Goals
Gathering Initial Insights
- Desk Research:
- To understand the broad user needs and goals, begin by collecting data from existing sources such as academic papers, industry reports, and published materials.

- Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Deploy tools like Likert scale questionnaires to gather quantitative data on user preferences, behaviors, and demographics. This helps in quantifying user expectations and satisfaction levels.
- User Interviews:
- Conduct structured, semi-structured, and user story interviews to gather deep insights into user perspectives and experiences. These interviews are crucial for understanding the personal nuances of user interactions with the product.
Start by following these steps to better understand user needs and goals and take the right approach.
Advanced Research Techniques
- Observation and Field Studies:
- Engage in contextual inquiry and ethnographic research to observe users in their natural environment. This direct observation is invaluable for gaining a realistic picture of user behavior and needs.

- Focus Groups:
- Organize focus group discussions to facilitate a guided conversation about specific topics or products. This qualitative data collection method helps in understanding the collective user perspective.
- Usability Testing:
- Implement both moderated and remote usability testing to evaluate the user experience of a product or interface. Observing users perform specific tasks can reveal critical insights into the usability and user-friendliness of the product.
As the second step in the process of understanding user needs and goals, conducting research techniques is crucial to moving forward with the user experience.
Analyzing and Applying Research Findings
- Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis:
- Use thematic analysis to interpret qualitative data from interviews and observations.
- Apply statistical methods like correlation and regression analysis to understand patterns and relationships in quantitative data collected through surveys and questionnaires.

- Synthesis of Research Data:
- Analyze and synthesize all gathered data to identify specific design requirements that address user needs. This step ensures that the design solutions are aligned with user expectations and adhere to user-centered design principles.
Choosing the right color theme for your website is crucial as it can significantly enhance the user experience. This article can help you select the perfect color scheme for your website. this article can help you to Select the Right Color Scheme for Your Website.
Identifying and Addressing User Needs
- Identifying User Needs:
- When interacting with a product or service, focus on understanding users’ desires, goals, preferences, and expectations. This understanding is crucial for creating designs that prioritize usability and user satisfaction.
- Challenges in User Needs Identification:
- Address challenges such as diverse user backgrounds, potential misalignments between user needs and design inputs, and the necessity for iterative design processes to refine and adapt solutions.

- Methods for Discovering User Needs:
- Utilize a combination of surveys, interviews, user observation, analytics, and persona development to uncover and validate user needs. This comprehensive approach helps in prioritizing features and functionalities that enhance user experiences.
By integrating these methodologies into the UX design process, you can ensure that your projects are not only user-friendly but also deeply aligned with the actual needs and goals of your users.
Developing User Personas and Journey Maps
User Personas: Crafting Comprehensive Profiles
- Creation Process:
- Personas are developed using insights gathered from user and stakeholder interviews, ensuring a deep understanding of the target audience.
- Key Elements of a Persona:
- Include critical details such as a photo, name, age, location, occupation, key frustrations, needs, and goals to bring the persona to life.

- Functionality Identification:
- Use personas to pinpoint the most crucial functionalities needed by the audience, enhancing the relevance and usability of the design.
- Sharing Insights:
- Communicate persona findings with stakeholders to align project goals and user expectations effectively.
User Journey Maps: Visualizing the User Experience
- Definition and Importance:
- A user journey map is a visual document that outlines the steps a user takes to achieve a goal, highlighting interactions, pain points, and emotions.
- Components of a Journey Map:
- Essential elements include the Person, Environment or Scenario, Journey Phases, Actions, Mindset, Emotions, and Opportunities for improvement.
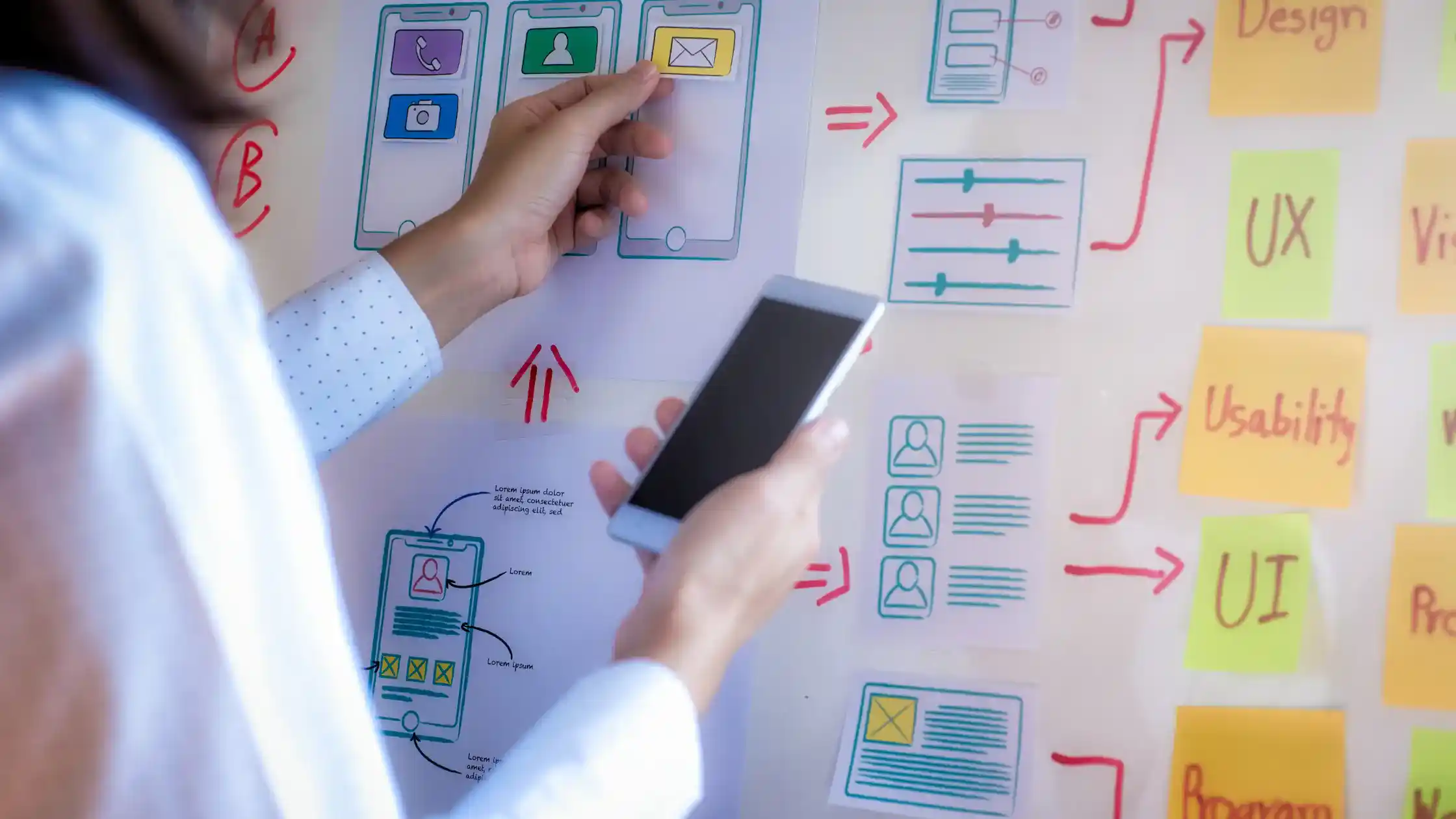
- Creating a Journey Map:
- Begin by identifying key milestones and documenting them on sticky notes. Consider related activities, actions, or touchpoints that occur during the user’s experience.
- Always include the user’s emotional responses to understand their experience better and identify potential improvements.
- Benefits of Journey Mapping:
- Journey maps facilitate storytelling, making the user’s experience easily understandable and relatable.
- The visual nature of journey maps helps in making the information memorable and easily digestible.
- By fostering empathy, journey maps allow design teams to see from the user’s perspective, crucial for enhancing user experience design.
Synthesizing Insights for Strategic Design
- Integrating Research Findings:
- Combine insights from user research, competitive analysis, and stakeholder inputs to create comprehensive personas and journey maps.
- Collaboration and Prioritization:
- Work closely with product managers, data scientists, and leads to prioritize features and define product requirements based on synthesized user data.

- Identifying Key User Experience Aspects:
- Use the developed personas and journey maps to pinpoint areas in the user experience that require more attention or improvement.
Wireframing and Prototyping
The Role of Wireframing in UX Design
- Foundation of UX/UI Projects: Wireframes are crucial as they provide a clear visual hierarchy, defining the layout, structure, and content placement of a digital interface.
- Visual Blueprints: Serving as visual representations, wireframes outline the structure and functionality of your product, focusing solely on usability and not on aesthetic details.

- Stages of Creation:
- Low-Fidelity: Sketches on paper that are rough and without scale.
- Medium-Fidelity: More accurate visual representations using design tools.
- High-Fidelity: Detailed elements like buttons, menus, and input fields with pixel-specific layouts.
Prototyping for Enhanced User Interaction
- Bringing Designs to Life: Prototypes add interactivity and functionality, making the design process more tangible and realistic for stakeholders.
- Range of Fidelity:
- Low-Fidelity: Basic prototypes used to explore design concepts.
- High-Fidelity: Advanced prototypes that are nearly final versions with full interactivity.

- Tools for Prototyping:
- Adobe XD: Allows for creating immersive clickable prototypes, which are essential for extensive testing.
- Other Popular Tools: Figma and Sketch are also widely used for wireframing and prototyping, offering a range of functionalities tailored to designer needs.
Integrating Wireframing and Prototyping into the UX Process
- Iterative Design Cycle: The UX design process is iterative, involving stages of research, problem definition, prototype building, testing, and refinement.

- Problem-Solving Early On Wireframing and prototyping allows for the early identification and resolution of design issues, which saves time and costs in the development phase.
- Collaborative Feedback: These techniques facilitate feedback from users and stakeholders, fostering better communication and idea generation among designers.
Practical Steps for Effective Wireframing and Prototyping
- Begin with Low-Fidelity Wireframes: Start exploring ideas through simple sketches to gauge the feasibility and effectiveness of design concepts.
- Develop Interactive Prototypes: Move to more detailed prototypes to conduct in-depth testing and validation, ensuring the design meets user needs.

- Use Advanced Tools: Leverage tools like Sketch and Balsamiq for wireframing and Adobe XD for prototyping to enhance the design process.
By following these structured steps and utilizing the right tools, you can ensure that your design not only meets user expectations but also remains aligned with business goals, effectively bridging the gap between conceptualization and final implementation.
Conducting User Testing
Defining Testing Objectives and Preparing the Test Plan
- Define Testing Objectives: Clearly outline your user testing goals and UX metrics. Decide what aspects of the user experience you want to test and what answers you expect to obtain.
- Draft a Test Plan: A comprehensive test plan should include the features, functionalities to be tested, and success or failure metrics. It’s crucial to identify these elements to measure the effectiveness of the design accurately.

Selecting and Preparing Participants
- Recruiting Participants: Choose unbiased participants who can provide honest feedback. Utilize platforms like usertesting.com or validately.com to find individuals who match your target user profile.
- Pre-study Questions: Begin the session by asking participants about their background and any relevant demographic or psychographic questions. This helps in setting the context for the testing.
Unlock the Power of HubSpot’s Customer Platform with a Free Demo – Your Smart Way to Success
Setting Up the Testing Environment
- Choose a Suitable Location: Conducting in-person testing is beneficial as it allows you to read body language and other subtle signals. A comfortable setting like a cafe or a real-world environment can enhance the focus and comfort of the participants.
- Replicate the Testing Environment: Ensure consistency in the testing process by using scripts and recreating the environment, including the timing and manner of interactions.

Conducting the Test
- Moderating the Test: Effective communication and careful preparation are key. Practice how you ask questions and create a comfortable environment to elicit valuable insights from users.
- Tasks and Scenarios: Provide participants with specific tasks using the prototype. Read scenarios that give context and ask them to perform tasks that reflect typical use cases.
Documenting and Analyzing Results
- Recording and Documentation: Use tools to record the session and document observations. A test documentation spreadsheet can be particularly useful in summarizing findings and identifying areas for improvement.
- Analyze the Findings: Gather all results, make sense of the data, and share summarized findings with your team. Prioritize issues based on their impact on user experience and identify possible solutions.

Utilizing Feedback for Refinement
- Feedback Integration: Use the insights gained from user testing to refine and improve the design. This might involve making iterations based on user feedback and retesting if necessary.
- Collaborative Review: Share the designs and test outcomes with cross-functional partners to understand the broader business impact and gather additional insights.
By adhering to these steps, you ensure that your design not only addresses the user’s needs but also aligns with broader business goals, thereby enhancing the overall user experience.
Implementation and Launch
Handing Over to the Development Team
- Arrange Design Handoff:
- Hand over the final design and comprehensive documentation to the development team to initiate the implementation phase.
- Collaboration with Developers:
- Maintain close collaboration with the development team to ensure that the implementation accurately reflects the design vision. Provide clear design specifications and assets for precise execution.

- Monitoring and Feedback:
- Continuously monitor user feedback and analytics post-launch to identify areas for further improvement. This ongoing assessment helps in refining the user experience based on real-world usage.
Make sure to read this article for essential information on the UX design process.
Ensuring Technical and User Experience Compliance
- Technical Constraints:
- Work in tandem with engineers to ensure that the designs meet the technical constraints and functionality requirements, facilitating a smoother transition from design to development.
- Launch Readiness:
- Confirm that the product launch aligns with business objectives and meets the established user experience and accessibility standards.

Long-Term Strategy and Continuous Improvement
- Sustained Relevance:
- Implement strategies to ensure that the product remains relevant and usable for the target audience over time. This involves making iterative refinements and updates based on evolving user needs and technological advancements.
- Ongoing Improvements:
- Commit to continuously improving the product through incremental changes, thereby enhancing the overall user experience and maintaining market competitiveness.
Implementation Process Overview
| Stage | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Design Handoff | Transfer of final designs and documentation to the development team. | |
| Collaboration and Monitoring | Ongoing collaboration with developers and monitoring of user feedback for quality assurance. | |
| Technical and UX Compliance | Ensuring designs adhere to technical specifications and user experience standards. | |
| Continuous Improvement | Regular updates and refinements based on user feedback and market changes. |
These steps will help you smoothly transition from design to development and deliver a high-quality user experience that meets current and future needs, If you’re new to web design and feeling lost about where to start, then you absolutely must check out this all-inclusive guide on how to become a web designer without a degree. It’s the perfect resource to help you get started with confidence!
FAQs
What are the primary stages involved in the UX design process?
The UX design process typically unfolds in five key stages:
1. Empathize: Understanding the users and their challenges deeply, often through interviews, observations, and empathy exercises.
2. Define: Clearly articulating the problem that needs to be addressed, often through creating user personas, defining user stories, and setting goals.
3. Ideate: Generating a range of creative solutions to the defined problem, usually through brainstorming sessions, sketching, and exploring different approaches.
4. Prototype: Building a preliminary version of the solution to visualize and test ideas, often using wireframes, mockups, or interactive prototypes.
5. Test: Evaluating the prototype with real users to gather feedback, validate assumptions, and refine the design iteratively.
Can you outline the phases of a UX project?
The UX project process can be broken down into four distinct phases:
1. UX Research: Beginning with a thorough investigation to understand user needs, behaviors, and pain points.
2. Design: Moving on to the actual creation of the design, including wireframing, prototyping, and visual design.
3. Iterative Testing: Continuously testing and validating the design with real users to identify and address any usability issues.
4. Development: Converting the finalized design into a functional product, often working closely with developers to ensure the design vision is implemented effectively.
What steps are involved in the UX process?
The UX process encompasses six critical steps:
1. Understand Customers: Grasping the users’ needs, behaviors, and preferences through various research methods such as interviews, surveys, and usability testing.
2. Research Competition: Analyzing what competitors are doing in terms of user experience, identifying strengths and weaknesses to inform the design process.
3. Sketch Product: Drafting the initial concept of the product through sketches, wireframes, or low-fidelity prototypes to explore different ideas and solutions.
4. Design Product: Crafting the detailed design of the product based on user research and feedback, focusing on usability, accessibility, and aesthetics.
5. Implementation: Applying the finalized design to a webpage or application, working closely with developers to ensure the design is implemented correctly.
6. Evaluation and Improvement: Assessing the product’s performance through usability testing, analytics, and user feedback, and making necessary enhancements to continuously improve the user experience.
What are the different phases of UX design research?
UX design research is composed of several key phases:
1. Discovery Phase: This phase includes user research, competitive analysis, and contextual inquiry, which all aim to gather insights about the user and the market.
2. Design Phase: Based on insights from the discovery phase, this phase focuses on creating and refining design solutions through ideation, prototyping, usability testing, and the establishment of information architecture and visual design.